Livy & Jupyter Notebook & Sparkmagic = Powerful & Easy Notebook for Data Scientist
livy is a REST server of Spark. You can see the talk of the Spark Summit 2016, Microsoft uses livy for HDInsight with Jupyter notebook and sparkmagic. Jupyter notebook is one of the most popular notebook OSS within data scientists. Using sparkmagic + Jupyter notebook, data scientists can execute ad-hoc Spark job easily.
Why livy is good?
According to the official document, livy has features like:
- Have long running SparkContexts that can be used for multiple Spark jobs, by multiple clients
- Share cached RDDs or Dataframes across multiple jobs and clients
- Multiple SparkContexts can be managed simultaneously, and they run on the cluster (YARN/Mesos) instead of the Livy Server for good fault tolerance and concurrency
- Jobs can be submitted as precompiled jars, snippets of code, or via Java/Scala client API
- Ensure security via secure authenticated communication
- Apache License, 100% open source
Why livy + sparkmagic?
sparkmagic is a client of livy using with Jupyter notebook. When we write Spark code at our local Jupyter client, then sparkmagic runs the Spark job through livy. Using sparkmagic + Jupyter notebook, data scientists can use Spark from their own Jupyter notebook, which is running on their localhost. We don’t need any Spark configuration getting from the CDH cluster. So we can execute Spark job in a cluster like running on a local machine.
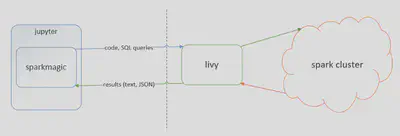
diagram from https://github.com/jupyter-incubator/sparkmagic/raw/master/screenshots/diagram.png
Requirements
- Spark Cluster
- Cloudera Director is nice to prepare
- Install git and maven
- I tried CDH 5.7 with CentOS 7
2. Local jupyter client
- virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper is awesome
Preparation
In order to use livy with sparkmagic, we should install livy into the Spark gateway server and sparkmagic into local machine.
- cloudera/livy: Livy is an open source REST interface for interacting with Apache Spark from anywhere
- jupyter-incubator/sparkmagic: Jupyter magics and kernels for working with remote Spark clusters
Install R
$ sudo yum install -y epel-release$ sudo yum install -y R
Build livy
$ git clone git@github.com:cloudera/livy.git$ cd livy$ mvn -Dspark.version=1.6.0 -DskipTests clean package
Because of failing test at that time, I added -DskipTests to build.
Run livy
Set environment variables as follows:
$ export SPARK_HOME=/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-5.7.1-1.cdh5.7.1.p0.11/lib/spark$ export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/etc/hadoop/conf
Add the following configuration into livy.conf:
livy.server.session.factory = yarn
Let’s run livy server
$ ./bin/livy-server
Open another terminal and check the server
$ curl localhost:8998/sessions{"from":0,"total":0,"sessions":[]}
As livy’s Default port number is 8998, we should open or forward the port.
Prepare sparkmagic in local machine
Install sparkmagic by following the document:
$ pip install sparkmagic$ jupyter nbextension enable --py --sys-prefix widgetsnbextension
Then install wapper kernel. Do pip show sparkmagic and you can see the Location info. In the following example, Location is /Users/ariga/.virtualenvs/ibis/lib/python3.5/site-packages.
$ pip show sparkmagic---Metadata-Version: 2.0Name: sparkmagicVersion: 0.2.3Summary: SparkMagic: Spark execution via LivyHome-page: https://github.com/jupyter-incubator/sparkmagic/sparkmagicAuthor: Jupyter Development TeamAuthor-email: jupyter@googlegroups.orgInstaller: pipLicense: BSD 3-clauseLocation: /Users/ariga/.virtualenvs/ibis/lib/python3.5/site-packagesRequires: ipywidgets, pandas, ipython, requests, mock, autovizwidget, numpy, nose, ipykernel, notebook, hdijupyterutilsClassifiers: Development Status :: 4 - Beta Environment :: Console Intended Audience :: Science/Research License :: OSI Approved :: BSD License Natural Language :: English Programming Language :: Python :: 2.6 Programming Language :: Python :: 2.7 Programming Language :: Python :: 3.3 Programming Language :: Python :: 3.4$ cd /Users/ariga/.virtualenvs/ibis/lib/python3.5/site-packages$ jupyter-kernelspec install sparkmagic/kernels/sparkkernel$ jupyter-kernelspec install sparkmagic/kernels/pysparkkernel
Copy the config.json into ~/.sparkmagic/config.json and modify it.
Run jupyter notebook
Before running jupyter, I recommend checking the connection from the local machine to the livy server.
$ curl YOUR_HOSTNAME:8998/sessions
Launch jupyter notebook and create PySpark notebook (of course you can use Spark)
$ jupyter notebook
The example notebook is here
Jupyter Notebook Viewer
_n MAXROWS: The maximum number of rows of a SQL query that will be pulled from Livy to Jupyter. If this number is…_nbviewer.jupyter.org
In the nbviewer, we can not see the result of SQL, but we can visualize the result of SQL with %%sql magic command. That’s awesome :)
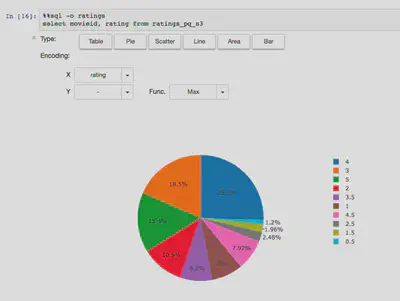
If you use %%local, you can use local Python libraries such as scikit-learn, seaborn etc, with received results from PySpark.